
This element was discovered in 1808 by L. J. Lussac and L. J. Thenard in Paris and independently by H. Davy in London. The name comes from Arabic buraq.
Ionization energies
BI 8.3 eV, BII 25.2 eV, BIII 37.9 eV.
Absorption fines of BI
The BI 2496(1) resonance doublet has been observed in the sun as a faint feature (Kohl et al. 1977). The line was also observed by Lemke et al. (1993) in three F-type stars. In two of them B is normal (and Li and Be are normal too), whereas in one B is weakened by at least -0.5 dex, whereas Li and Be are highly depleted (-1.7 dex).
Absorption lines of BII
Beosgaard and Heacox (1978) observed the resonance line at 1362(1) in 16 B- and A-type stars. The feature has W between 0.100 for B1III and 0.060 for B 3 V.
Behavior-in non-normal stars
Sadakane et al. (1985) analyzed the ultraviolet resonance line 1362 of BII in Bp stars of the Hg-Mn subgroup and found a wide variety of B strengths, from W = 0 to strong lines with W = 0.150.
Molaro (1987) set an upper limit far B in one subdwarf of one tenth of the solar value.
Duncan et al. (1993)
observed three halo dwarfs and found B/Be
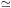 10, which
corresponds approximately to the solar value.
10, which
corresponds approximately to the solar value.
Isotopes
B has two stable isotopes, B10 and B11. The solar ratio B10 / B11 is about 0.25. There exist four shorter lived isotopes.
The isotopic ratio could be derived from the BI resonance line, where the isotopic shift is 0.025 Å.
Origin
B is produced by cosmic ray spallation.
Published in "The Behavior of Chemical Elements in Stars", Carlos Jaschek and Mercedes Jaschek, 1995, Cambridge University Press.